线程或进程独占 CPU 一般用来相对地提升实时性, 但也不要指忘达到真正的实时操作系统的性能.
进程邦定 CPU
我们通过系统调用 sched_setaffinity 进行绑定,通过 sched_getaffinity 获取绑定关系。注意这对方法是进程级别的绑定。代码中指定 cpu0 和 cpu3,我们可以通过 htop 查看,两个 cpu 使用达到了 100%,其他的 cpu 均不会(正常场景)。
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void* testfunc(void* t) {while(1);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
cpu_set_t mask;
printf("pid=%d\n", getpid());
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(0, &mask);// 将 cpu0 绑定
CPU_SET(3, &mask);// 将 cpu3 绑定
sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &mask) ;
pthread_t tid1;// 创建线程 1
if (pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, (void *)testfunc, NULL) != 0)
{fprintf(stderr, "thread create failed\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_t tid2;// 创建线程 2
if (pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, (void *)testfunc, NULL) != 0)
{fprintf(stderr, "thread create failed\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
return 0;
}
线程邦定 CPU
对于线程绑定,我们需要借助 pthread 库,通过函数 pthread_setaffinity_np 来设置绑定 cpu 关系。我们通过 htop 查看,会放发现 cpu0 和 cpu3 使用率达到 100%。
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void* testfunc(void* t) {
int i = 3;
while(i) {sleep(5);
printf("tid=%d,cpu=%d\n",pthread_self(), sched_getcpu());
i--;
}
while(1);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
cpu_set_t mask;
printf("pid=%d\n", getpid());
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
pthread_t tid1;
if (pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, (void *)testfunc, NULL) != 0)
{fprintf(stderr, "thread create failed\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_t tid2;
if (pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, (void *)testfunc, NULL) != 0)
{fprintf(stderr, "thread create failed\n");
return -1;
}
printf("tid1=%d,tid2=%d\n", tid1,tid2);
CPU_SET(0, &mask);// 绑定 cpu0
pthread_setaffinity_np(tid1, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &mask) ;
// 清除之前设置,重新设置绑定 cpu3
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
CPU_SET(3, &mask);
pthread_setaffinity_np(tid2, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &mask) ;
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
return 0;
}
配置内核禁止调度到某些核心
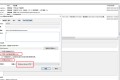
上面的设置只能保证进程或者线程运行在特定的 cpu 上,但仍然不能独自享有,时间片到了也是有可能被切换出去。那么有什么方法将可以独占某个 cpu 呢?答案是肯定。我们可以设置 linux 启动参数 grub,在启动参数后面增加isolcpus=a,b,c。具体修改如下:

编辑 grub 文件后再执行该命令 grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg 更新 grub,重要,重要,重要。
这样在系统启动后,操作系统就不会把任务调度到 cpu0 和 cpu3 上。但是我通过 htop 观察 cpu0、cpu3 使用率,并非始终是 0,而是有略微的变化,后来经过查询相关说明,内核线程任然会调度到 cpu0 和 cpu3 上。也就是说这种方式只能控制用户进程。
接下我们就可以通过 sched_setaffinity 方式进行绑定,以达到独占效果,但是操作 grub 要非常谨慎,搞不好系统会起不来啊
正文完



![用C51实现带奇偶校验的串行通信[转]](https://justchen.com/wp-content/themes/wordpress-theme-puock-2.8.5/timthumb.php?w=120&h=80&a=c&zc=1&q=90&src=https://justchen.com/wp-content/themes/wordpress-theme-puock-2.8.5/assets/img/random/4.jpg)